The Importance of Medium- and Heavy-Duty Electrification
Medium- and heavy-duty vehicles (MHDVs) are the backbone of the transportation and logistics industries. Changing these vehicles is critical for fleet electrification. They include vehicles in Classes 3 through 8, such as delivery trucks and long-haul freight vehicles, which play a vital role in moving goods. Despite their utility, MHDVs contribute disproportionately to greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for approximately 25% of road transportation emissions while representing a fraction of the vehicles on the road. A Class 8 truck, for example, emits five times more CO₂ than a light-duty vehicle, making their electrification a critical step toward achieving sustainability goals (Electrada, 2023).
Current Challenges in Electrifying MHDVs Critical for Fleet Electrification
Adoption of electric MHDVs remains limited due to several challenges:
- High Upfront Costs: Electric MHDVs are more expensive than their diesel counterparts, largely due to battery costs.
- Infrastructure Requirements: MHDVs require high-capacity charging stations, which can be expensive and complex to deploy.
- Limited Availability: The market offers fewer electric options in these classes compared to light-duty vehicles.
According to Electrada’s 2023 survey, only 16.3% of fleets have invested in Class 3-5 EVs, and just 6.8% have adopted Class 6-8 EVs. These barriers highlight the need for innovative solutions and supportive policies to accelerate adoption (Electrada, 2023).
Why Now Is the Time to Act
Advancements in technology and financial incentives are making electrification more feasible:
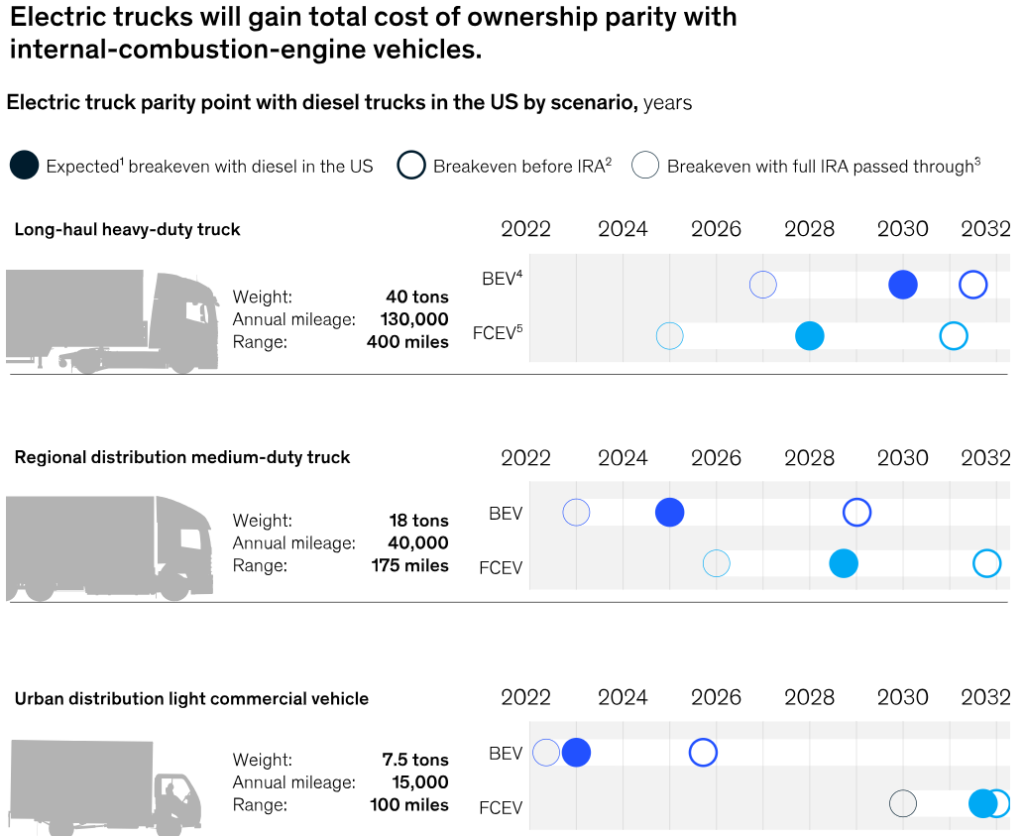
- Falling Battery Costs: Battery prices have dropped by 89% since 2010, significantly improving the total cost of ownership (TCO) for electric vehicles. McKinsey predicts TCO parity for medium-duty EVs by 2025 and for heavy-duty EVs by 2030 (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
- Incentives and Policies: Federal and state programs offer tax credits for electric vehicles and charging infrastructure, reducing upfront costs.
- Charging-as-a-Service (CaaS): Providers like Electrada simplify charging infrastructure deployment, handling installation and maintenance under a predictable pricing model (Electrada, 2023).
Benefits of Early Adoption
Early adopters of MHDV electrification stand to gain:
- Operational Savings: Reduced fuel and maintenance costs contribute to significant long-term savings.
- Regulatory Readiness: Meeting future emissions regulations ahead of schedule reduces compliance risks.
- Enhanced Brand Perception: Adopting sustainable practices aligns with customer and investor expectations.
Conclusion
Electrifying medium- and heavy-duty vehicles is no longer a question of if but when. With falling costs, emerging technologies, and strong policy support, fleets that invest in MHDV electrification today will benefit from cost savings, reduced emissions, and a competitive edge.
Works Cited
Electrada. “The State of Fleet EV Adoption.” Electrada, 2023, electrada.com
McKinsey & Company. “Why the Economics of Electrification Make This Decarbonization Transition Different.” McKinsey & Company, 2023, www.mckinsey.com.
_ _
Written by Taylor Steele
January 2024




